Contents
- 1 The Dairy Dilemma: Weighing the Pros and Cons of Dairy Products in Our Diets
- 2 The Benefits of Dairy Products
- 3 Lactose intolerance and other digestive issues
- 4 High levels of saturated fat can lead to heart diseases
- 5 Environmental impact
- 6 Nutritional Value
- 7 Bone Health Benefits
- 8 Energy Boosting Properties
- 9 The Cons of Dairy Products
- 10 Conclusion:
The Dairy Dilemma: Weighing the Pros and Cons of Dairy Products in Our Diets
Brief Overview of Dairy Products
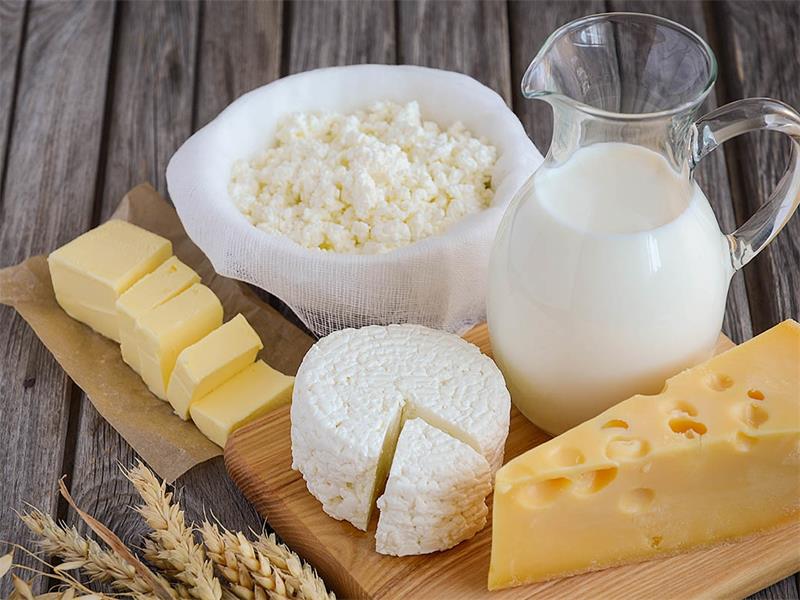
Dairy products, such as milk, cheese, and yogurt, come from the mammary glands of mammals. In modern society, most dairy products come from cows, although sheep, goats, and even camels are also used for milk production around the world. Dairy products are a staple in many cuisines and cultures worldwide.
They are commonly used in cooking and baking recipes due to their unique properties that can add moisture or richness to dishes. Additionally, many people consume dairy products on their own or as a part of a meal for their nutritional benefits.
Importance of Dairy Products in Our Diet
Dairy products contain essential nutrients that our bodies need to thrive. Calcium is one primary nutrient that comes from dairy and is important for building strong bones and teeth.
Additionally, dairy contains vitamin D which helps our bodies absorb calcium. Protein is another nutrient present in dairy products that helps our muscles grow and repair themselves after physical activity or injury.
Carbohydrates found in dairy help give us energy throughout the day. However, it is important to note that not all people can tolerate lactose found in dairy products.
Lactose intolerance occurs when the body cannot properly digest lactose sugar found in milk due to a deficiency of lactase enzymes within the small intestine’s walls. Nonetheless, for those who can consume dairy without problems, it can provide valuable nutrients for good health.
The Benefits of Dairy Products
Dairy products are known for their importance in a healthy and balanced diet. They provide essential nutrients such as calcium, Vitamin D, protein, and other minerals that our body needs to function properly. In this section, we will explore the benefits of dairy products and why they should be included in our daily diet.
Good source of calcium and other essential nutrients
Calcium is a crucial mineral that our bodies need to build strong bones and teeth. Dairy products are an excellent source of calcium, making them an important part of a healthy diet.
One cup of milk contains about 30% of the recommended daily intake (RDI) of calcium. Cheese is also a good source of calcium; one ounce (28g) of cheddar cheese contains 20% RDI.
Apart from calcium, dairy products are also rich in other essential nutrients such as Vitamin D, riboflavin (Vitamin B2), phosphorus, potassium, magnesium and zinc. For example, a cup (240ml) serving of milk provides 25% RDI for Vitamin D, which is crucial for bone health, especially in older adults.
Helps in building strong bones and teeth
As mentioned earlier, the high levels of calcium in dairy products help build strong bones and teeth. This is especially important during childhood when children’s bones are still developing.
Studies have shown that children who consume adequate amounts of dairy products have higher bone density than those who don’t. In addition to calcium content, phosphate is another mineral found in milk that can contribute to bone health by helping with bone remodeling processes.
Provides energy and aids in weight management
Dairy products also supply energy to the body through carbohydrates found mainly as lactose sugar. Lactose is broken down into glucose which fuels the body cells with needed energy. Moreover, dairy products have been shown to play a role in weight management.
Research suggests that high-calcium diets may help reduce body weight and promote fat loss. Proteins in dairy products such as casein and whey also have satiating effects which can help reduce appetite and promote feelings of fullness leading to less food intake during the day.
The benefits of dairy products are numerous, not only for bone health but also for energy supply and weight management. It is important to include them in a balanced diet while also being mindful of any underlying health conditions that could affect individual tolerance or absorption rates of nutrients they contain.
Lactose intolerance and other digestive issues
One of the most common cons of consuming dairy products is that many people are lactose intolerant, meaning their bodies lack the enzyme necessary to break down lactose, a sugar found in milk. This can result in uncomfortable digestive symptoms such as bloating, gas, and diarrhea.
It’s estimated that about 65% of the world’s population has some degree of lactose intolerance. Aside from lactose intolerance, dairy products can also cause other digestive issues for some people.
For example, some individuals may experience acid reflux symptoms after consuming dairy. Others may have an allergic reaction to proteins found in milk, leading to hives or even anaphylaxis.
If you suspect you may have difficulty digesting dairy products, it’s important to talk to your doctor or a registered dietitian. They may recommend alternatives such as lactose-free milk or non-dairy sources of calcium.
High levels of saturated fat can lead to heart diseases
Another potential downside to consuming dairy products is their high levels of saturated fat. While some types of fat (such as monounsaturated and polyunsaturated) are healthy in moderation, saturated fats have been linked with an increased risk for heart disease.
Many dairy products are high in saturated fat – for example, a cup of whole milk contains almost 5 grams. Cheese and butter are also notoriously high in saturated fat content.
To reduce your risk for heart disease while still enjoying dairy products, experts recommend opting for low-fat or skim varieties whenever possible. You can also try replacing some servings with non-dairy sources of calcium such as leafy greens or fortified plant milks.
Environmental impact
It’s worth considering the environmental impact associated with producing dairy products on a large scale. Firstly, producing cows’ milk requires large amounts of resources including water (it takes around 1,000 liters of water to produce one liter of milk) and land.
This can contribute to deforestation and other sustainability issues. Additionally, cows themselves can generate significant amounts of methane – a greenhouse gas – through their digestive processes.
According to the United Nations’ Food and Agriculture Organization, livestock accounts for around 14.5% of all human-induced greenhouse gas emissions. While it’s unlikely that most people will stop consuming dairy products entirely, being mindful of the environmental impact associated with dairy products can be an important consideration as we strive for more sustainable lifestyles.
Nutritional Value
Dairy products have an impressive nutritional profile that makes them a valuable addition to any diet. Milk, cheese, and yogurt are all excellent sources of calcium, Vitamin D, and protein. Calcium is essential for healthy bones and teeth, while Vitamin D plays a crucial role in bone health by helping the body absorb calcium.
Protein is essential for building and repairing tissues in the body. In addition to calcium, Vitamin D, and protein, dairy products also contain other nutrients such as phosphorus, magnesium, zinc, and potassium.
These nutrients are vital for various bodily functions such as nerve function, muscle contraction, and blood pressure regulation among others. A single serving of dairy products can provide up to 30% of the recommended daily intake of calcium and vitamin D. Therefore including dairy products in your diet can help ensure that you get enough essential nutrients.
Bone Health Benefits
One of the most significant benefits of consuming dairy products regularly is its ability to promote bone health. The high levels of calcium found in milk and other dairy products make them an excellent food choice for individuals looking to maintain strong bones throughout their life. Calcium works together with other minerals like phosphorus and magnesium to keep bones strong by maintaining bone density.
Studies suggest that consuming three servings of dairy per day may reduce the risk of fractures later in life. Moreover, the consumption of low-fat milk has been shown to help prevent osteoporosis- a condition where bones become brittle due to loss of tissue.
Energy Boosting Properties
Not only are dairy products high in essential nutrients like calcium but they also contain carbohydrates that provide energy needed for daily activities such as walking or exercising. Additionally,dairy can provide a quick energy boost due to its natural sugars – lactose – which gets quickly absorbed into the bloodstream providing instant energy needed when fatigued or hungry.
The combination of carbohydrates and fats found in dairy products makes it an ideal pre-workout or post-workout snack, providing both energy and nutrients necessary for muscle recovery. Thus, making it a good food choice for athletes and individuals looking to maintain high energy levels throughout the day.
The Cons of Dairy Products
Lactose Intolerance & Digestive Issues: The Unfortunate Side Effect
While dairy is a great source of essential nutrients, some people experience unpleasant digestive symptoms after consuming dairy products. This is due to lactose intolerance, which occurs when the body doesn’t produce enough lactase enzyme to break down lactose (a sugar found in milk).
Symptoms of lactose intolerance include bloating, gas, diarrhea, and stomach cramps. It’s estimated that around 65% of the world’s population has some degree of lactose intolerance.
While this condition may not be life-threatening, it can definitely put a damper on your day if you’re one of the many people who suffer from it. Fortunately, there are alternatives available such as lactose-free milk and dairy-free products like almond or soy milk.
Saturated Fat Content & Heart Diseases: A Cause for Concern?
One concern about dairy products is their high levels of saturated fat. Saturated fat has been linked to increased risk of heart disease and stroke.
However, recent studies have shown that saturated fats may not be as harmful as previously believed. It’s important to note that not all saturated fats are created equal.
The type found in dairy (palmitic acid) may have different effects on cholesterol levels than other types found in processed foods (like trans fats). Additionally, many studies have shown no significant association between dairy consumption and heart disease risk.
That being said, it’s still important to practice moderation when consuming high-fat foods like cheese or butter. Opting for low-fat or non-fat varieties can also help reduce your intake of saturated fat.
Environmental Impact: Moo-ving Towards Sustainability
Another downside to dairy production is its environmental impact. Dairy cows require large amounts of water and feed to produce milk. Additionally, their manure releases methane (a potent greenhouse gas) into the atmosphere.
According to a study by the United Nations, livestock production (including dairy) accounts for around 14.5% of global greenhouse gas emissions. Additionally, runoff from dairy farms can pollute nearby water sources and harm aquatic life.
To reduce the environmental impact of dairy production, it’s important to support sustainable practices like grass-fed cows and organic farming. Additionally, reducing overall meat consumption (including dairy) can have a significant impact on reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
Conclusion:
After weighing the pros and cons of consuming dairy products, it is important to note that it can be a nutritious addition to one’s diet when consumed in moderation. Dairy products are packed with essential vitamins and nutrients like calcium, vitamin D, and protein that play an important role in maintaining good health.
However, it is crucial to be aware of the negative aspects of dairy consumption as well. Lactose intolerance can affect a large portion of the population, leading to digestive issues.
The high levels of saturated fat in some dairy products can also contribute to heart diseases if consumed excessively. Additionally, there are environmental concerns surrounding dairy production such as carbon emissions and water usage.
Encouraging Moderation
Moderation is key when it comes to incorporating dairy into your diet. It is recommended that individuals consume 2-3 servings a day from all food groups combined – including milk, cheese or yogurt – depending on age and activity levels. Consuming different types of dairy products also helps provide variety in your diet while still gaining the benefits.
Dairy Alternatives
If you’re lactose intolerant or prefer not to consume animal products for ethical reasons, there are plenty of alternatives available in the market today such as almond milk, soy milk or coconut milk which are fortified with essential nutrients like calcium and vitamin D.
An Optimistic Spin
The debate over whether or not we should consume dairy remains ongoing with strong arguments on both sides. However, by being mindful of our intake levels while enjoying the benefits of these nutrient-rich foods in moderation combined with diversity from other sources may lead us towards a healthier lifestyle.