Contents
- 1 The Science Behind Aging and Free Radicals
- 2 What are antioxidants?
- 3 The Power of Antioxidants
- 4 What are Antioxidants?
- 5 Definition of antioxidants and their role in the body
- 6 Examples of common antioxidants found in food
- 7 How Do Antioxidants Work?
- 8 Benefits of Antioxidants
- 9 Foods High in Antioxidants
- 10 Supplements vs Whole Foods
- 11 Common Misconceptions about Antioxidants
- 12 Debunking common myths about antioxidant consumption
- 13 Conclusion
The Science Behind Aging and Free Radicals
As we age, our body undergoes several changes that lead to physical and cognitive decline. One of the primary contributors to this aging process is the accumulation of free radicals in our bodies.
Free radicals are highly reactive molecules that damage cells and tissues by stealing electrons from other molecules, causing a chain reaction that leads to oxidative stress. This oxidative stress caused by free radicals can result in various diseases, accelerate aging, and damage DNA.
Antioxidants are essential because they help neutralize these free radicals by donating an electron without becoming unstable themselves. This process breaks the chain reaction before it can cause more harm.
What are antioxidants?
Antioxidants are compounds found naturally in foods such as fruits, vegetables, nuts, and grains or in supplements, which help protect cells from damage caused by free radicals. These compounds work by neutralizing free radicals before they can cause more significant harm to your body.
Some common antioxidants include vitamins C and E, beta-carotene, selenium, lycopene, and many more. Each type of antioxidant has a unique function and works differently within your body.
The Power of Antioxidants
By consuming foods rich in antioxidants or taking antioxidant supplements regularly, you can help slow down the aging process caused by oxidative stress while improving your overall health. Antioxidants have been shown to have numerous benefits such as protecting against chronic diseases like cancer and heart disease while also boosting your immune system.
In addition to their numerous health benefits, antioxidants also play a role in maintaining healthy skin. They protect the skin from UV light exposure-induced damage while also preventing premature wrinkling.
Understanding how free radicals cause aging and how antioxidants work is essential for maintaining good health throughout life. The following sections of this article will discuss specific types of antioxidants found in food sources along with their benefits, ways to incorporate them into your diet, and common misconceptions about antioxidant consumption.
What are Antioxidants?
Antioxidants are substances that protect our cells from the damage caused by free radicals. Free radicals are unstable molecules that can cause harm to our cells, leading to oxidative stress, inflammation, and cell damage. Antioxidants work by neutralizing free radicals and preventing them from causing harm to our bodies.
Antioxidants are naturally produced by our bodies, but they can also be obtained from the food we eat and supplements we take. Common antioxidants found in food include vitamins A, C, and E, beta-carotene, selenium, lycopene, and flavonoids.
Definition of antioxidants and their role in the body
Antioxidants play a crucial role in maintaining our overall health. They protect our cells from damage caused by free radicals which can lead to chronic diseases such as cancer, heart disease, and Alzheimer’s disease among others. When free radicals attack healthy cells in our body through a process called oxidation it causes cell death or mutation.
This is where antioxidants come in – they donate an electron to the free radical thereby “neutralizing” it before it attacks any healthy cells. In addition to their ability to fight against oxidative stress and inflammation; Antioxidants also help support healthy aging by protecting against age-related diseases such as macular degeneration among other conditions.
Examples of common antioxidants found in food
Some common examples of foods rich in antioxidants include berries like blueberries & raspberries which contain high levels of anthocyanins- a type of flavonoid Compound; dark chocolate which contains flavonols; spinach which is rich in Vitamin E; green tea which contains catechins; tomatoes rich in Lycopene among others. It is essential for us all to consume antioxidant-rich foods regularly so as not only to boost overall health but also to strengthen the immune system. Incorporating these nutrient-rich foods into our diets can help us maintain optimal well-being and prevent chronic diseases in the future.
How Do Antioxidants Work?
Antioxidants play a crucial role in fighting free radicals and preventing oxidative damage in the body. Free radicals are highly unstable molecules that can cause cellular damage and accelerate aging if they aren’t neutralized by antioxidants. This is where antioxidants come in – they work to stabilize free radicals by donating an electron to the molecule, which prevents it from causing further damage.
There are several different types of antioxidants, each with a unique function. For example, vitamin C is water-soluble and works to protect the inside of cells and tissues from oxidative stress.
Vitamin E is fat-soluble and protects cell membranes and lipids from oxidative damage. Meanwhile, carotenoids like beta-carotene are important for protecting the skin from UV-induced oxidative damage.
Discussion on the Different Types of Antioxidants
As mentioned above, there are many different types of antioxidants with various functions in the body. Here are some examples: – Vitamin C: Found in citrus fruits, strawberries, kiwi, broccoli, and peppers.
– Vitamin E: Found in almonds, sunflower seeds, avocadoes, spinach, and sweet potatoes. – Beta-carotene: Found in carrots, sweet potatoes,s kale, mangoes, and apricots
– Selenium: found in brazil nuts, tuna, liver, etc. – Flavonoids: founds in berries, nuts, chocolate, etc.
These are just a few examples of the many types of antioxidants out there. In general, it’s recommended to consume a variety of antioxidant-rich foods to obtain these benefits.
Specific Functions of Antioxidants
Different types of antioxidants have specific functions within the body. For instance, the skin needs the antioxidant beta-carotene that we get when we consume orange-colored foods such as carrots, pumpkins, etc. It helps repair skin cells, reduces inflammation, and protects against sun damage. Vitamin C on the other hand plays an important role in collagen synthesis, which is a crucial component of connective tissue that supports skin health. , vitamin E is vital for protecting cell membranes and lipids from oxidative damage, which can help prevent certain types of cancer.
It also helps improve eye health and may reduce the risk of age-related macular degeneration. All in all, antioxidants are essential components to maintaining optimal health.
Benefits of Antioxidants
Antioxidants are essential nutrients that can help prevent and even repair cellular damage caused by free radicals. By neutralizing these harmful molecules, antioxidants have the potential to provide numerous health benefits. Here are some ways that consuming antioxidant-rich foods or supplements can benefit your health:
Improve Skin Health
Antioxidants can help protect your skin from oxidative stress caused by environmental factors such as pollution, UV radiation, and poor diet. This oxidative stress can lead to premature aging and other skin problems such as wrinkles, age spots, and fine lines.
One antioxidant that has been shown to be particularly effective in improving skin health is vitamin C. This powerful nutrient helps to stimulate collagen production, which is essential for maintaining firm and youthful-looking skin. Other antioxidants like vitamin E and beta-carotene also play an important role in protecting against photoaging (damage caused by UV radiation).
Boost Immunity
Free radicals can damage your immune cells, making it harder for your body to fight off infections and illnesses. Antioxidants help to prevent this damage by neutralizing free radicals before they cause harm.
One study found that supplementing with vitamin C improved the function of immune cells in people who were under high levels of stress. Other studies have suggested that antioxidants like quercetin and zinc may also help support a healthy immune system.
Prevent Chronic Diseases
Free radicals have been linked to a variety of chronic diseases including cancer, heart disease, diabetes, and Alzheimer’s disease. Consuming a diet rich in antioxidants has been shown to reduce the risk of developing these diseases.
For example, one study found that people who ate more fruits and vegetables (which are high in antioxidants) had a lower risk of developing heart disease compared to those who ate fewer fruits and vegetables. Another study found that supplementing with vitamin E reduced the risk of developing prostate cancer in men.
Overall, consuming antioxidants through your diet or supplements can provide a range of health benefits. From improving skin health to boosting immunity and preventing chronic diseases, incorporating antioxidant-rich foods into your diet is a simple yet effective way to take care of your body.
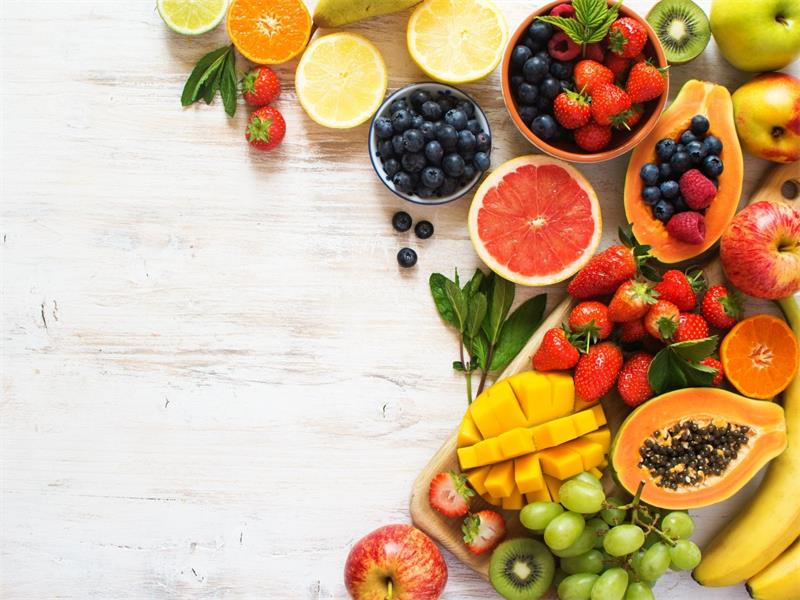
Foods High in Antioxidants
The Ultimate List of Antioxidant-Rich Foods
When it comes to incorporating antioxidants into your diet, there are plenty of delicious options to choose from. Fruits, vegetables, nuts, and spices are all great sources of antioxidants that can help fight free radicals and slow down the aging process.
Here is a list of some of the top antioxidant-rich foods: – Berries: Blueberries, blackberries, raspberries, and strawberries are all packed with antioxidants.
These sweet treats can be enjoyed on their own or added to smoothies or yogurt for an extra boost. – Dark Chocolate: Yes, you read that right!
Dark chocolate is a great source of antioxidants and can also provide other health benefits such as improving heart health. – Leafy Greens: Spinach, kale, collard greens – these leafy veggies are not only high in iron but also contain tons of antioxidants.
– Nuts: Almonds, walnuts, and pistachios are just a few examples of nuts that contain high levels of antioxidants. They make for a great snack or can be added to salads for some extra crunch.
Incorporating Antioxidant-Rich Foods into Your Diet
Now that you know which foods are high in antioxidants let’s talk about how to easily incorporate them into your daily diet. One simple way is to add berries or sliced fruit as a topping to your morning cereal or oatmeal. You could also try swapping out unhealthy snacks for nuts or making your own trail mix with dried fruits and nuts.
Another way to increase your intake is by adding leafy greens such as spinach or kale to your daily meals – try adding spinach leaves to sandwiches instead of lettuce! You could also mix up a salad using antioxidant-rich ingredients like pomegranate seeds or orange slices.
One creative way to include antioxidants in your diet is by adding spices like cinnamon or turmeric to your meals. Cinnamon can be sprinkled on top of oatmeal or used as an ingredient in baking, while turmeric can be added to curries or soups for an extra boost of flavor and antioxidants.
Supplements vs Whole Foods
Comparison between taking antioxidant supplements versus consuming whole foods high in antioxidants
While consuming whole foods high in antioxidants is the most natural way to boost your antioxidant levels, sometimes it is not enough. This is where antioxidant supplements come into play.
Supplements are a convenient way to get higher doses of antioxidants without having to eat large quantities of food or prepare complicated meals. However, there are pros and cons for each option.
Pros and Cons for Each OptionWhole Foods:
One of the benefits of getting antioxidants from whole foods is that you’ll also get other beneficial nutrients that come with them such as vitamins, minerals, fiber, and phytonutrients. These nutrients work together in synergy to provide more health benefits than just taking a supplement that provides only one type of antioxidant.
On the downside, it can be difficult to consume enough whole foods high in antioxidants every day. It may require a lot of time planning meals and preparing food. Supplements:
Antioxidant supplements offer a quick and easy way to increase your antioxidant intake without having to consume large amounts of food. Additionally, some people may have difficulty digesting certain foods or have dietary restrictions that make it hard for them to consume enough antioxidants through diet alone.
However, taking too many supplements can be harmful as excessive amounts can lead to toxicity or interfere with medication absorption. Also, most supplements only contain one or two types of antioxidants which may not provide the same synergistic health benefits as getting them from whole foods.
Both options have their advantages and disadvantages depending on individual needs and lifestyle factors. It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplementation regimen or making significant changes to your diet plan.
Common Misconceptions about Antioxidants
The More Antioxidants, the Better
One of the most common misconceptions about antioxidants is that more is always better. In reality, consuming excessive amounts of antioxidants, especially through supplements, can actually be harmful to your health.
Studies have shown that taking high doses of certain antioxidants, such as vitamin E and beta-carotene, can increase your risk of cancer and other chronic diseases. It’s important to consume antioxidants within a balanced diet rather than relying on supplements alone.
All Antioxidants are Created Equal
Another misconception is that all antioxidants are created equal. While many different types of antioxidants exist, each with its own unique properties and functions, not all provide the same benefits. For example, some studies have shown that certain types of flavonoids found in tea and citrus fruits may help improve heart health and reduce inflammation more effectively than other types.
Antioxidants are a Cure-All
Many people believe that consuming large amounts of antioxidant-rich foods or supplements can eliminate all health problems and ward off disease completely. However, while antioxidants can certainly provide numerous health benefits when consumed as part of a balanced diet and healthy lifestyle habits such as regular exercise and stress management, they are not a cure-all solution for every ailment. It’s important to remember that maintaining overall good health requires a comprehensive approach that includes multiple factors such as diet quality, physical activity levels, sleep habits, and stress management.
Debunking common myths about antioxidant consumption
Antioxidant Supplements Provide More Benefits Than Whole Foods
One common myth surrounding antioxidant consumption is that taking supplements provides greater benefits than consuming whole foods high in antioxidants. However research suggests otherwise – studies have consistently shown that individuals who consume diets rich in whole foods high in antioxidants have a lower risk of chronic diseases like cancer and heart disease than those who rely on supplements alone. Moreover, whole foods like fruits and vegetables also provide many other important nutrients, fiber, and water that are crucial for overall health.
You Can Overdose on Antioxidants from Whole Foods
Another myth is that you can overdose on antioxidants from consuming too many antioxidant-rich whole foods. However, this is not the case as the body has a built-in regulatory system to help maintain balance and prevent excess accumulation. Unlike supplements which can come in high doses, it’s nearly impossible to consume too many antioxidants from whole foods alone without overeating or consuming excessive amounts of certain types of foods.
Antioxidants Don’t Interact with Other Nutrients
Some people believe that antioxidants don’t interact with other nutrients in food and function independently. However, research indicates that certain combinations of nutrients can enhance each other’s effects when consumed together.
For example, consuming vitamin C-rich foods such as oranges with iron-rich grains or legumes can increase iron absorption in the body due to vitamin C’s role in enhancing non-heme iron absorption. The key takeaway is that consuming a variety of nutrient-dense whole foods rather than relying on supplements alone is important for overall health and optimal nutrient absorption.
Conclusion
Antioxidants are a crucial component to maintaining a healthy lifestyle and slowing down the aging process. By combating free radicals, they protect our cells from oxidative damage and help prevent chronic diseases.
We’ve covered the definition of antioxidants and their role in neutralizing free radicals. We’ve discussed the many health benefits associated with consuming antioxidant-rich foods such as improved skin health, boosted immunity, and reduced risk of chronic diseases such as cancer and heart disease.
We also looked at the different types of antioxidants found in various foods. It’s important to note that while taking supplements can be beneficial for some people, whole foods high in antioxidants should always be your primary source.
Incorporating fruits, vegetables, nuts, and spices into your diet can have a significant impact on your overall health. It’s important to debunk common misconceptions about antioxidants- namely that consuming large amounts will immediately reverse damage or cure diseases.
Antioxidants are not a magic bullet but rather work best when consumed consistently over time as part of an overall healthy lifestyle. With all this information at hand, we hope you’re inspired to include more antioxidant-rich foods in your diet to promote optimal health and aging!